Response of extratropical cyclone activity to the
Kuroshio large meander in northern winter
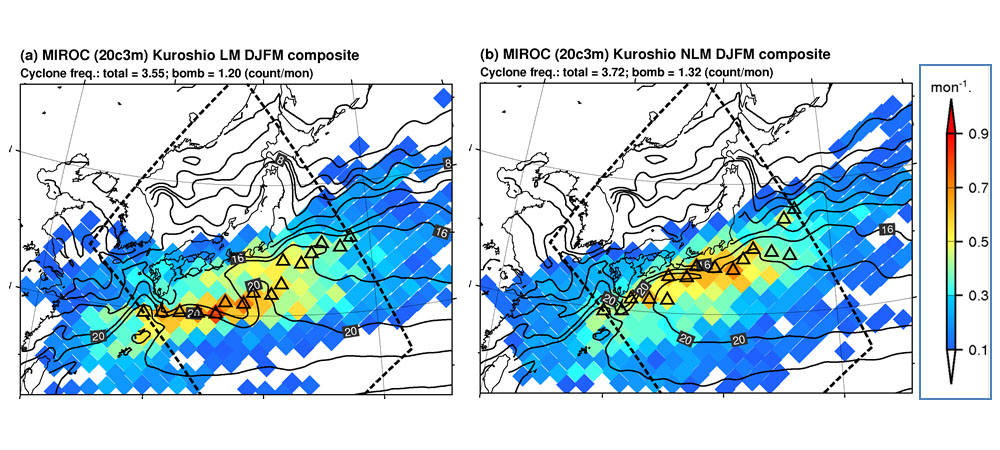
We examined possible responses of cyclone activities to the bimodal path
states of the Kuroshio Current (i.e., large-meander (LM) and non-LM (NLM))
by using the long-term reanalysis data and the twentieth century hindcast
experiment of atmosphere-ocean coupled model. Compared with a seasonal
mean cyclone track frequency for the LM and NLM periods, a primary cyclone
track shifts southward in association with the meander of Kuroshio Current.
Composite analyses of the hindcast experiment showed remarkable atmospheric
responses accompanying the Kuroshio LM. The Kuroshio LM causes
a decrease in latent heat flux in the south of Japan and a southward shift
of the near-surface baroclinic zone. Distinctive decreases in thermodynamic
fluxes inhibit the rapid development of cyclones in the meander region, eventually
inducing positive sea level pressure anomalies downstream from that
region.
黒潮の大蛇行・非大蛇行に対する冬季の温帯低気圧活動の応答について、大気再解析データおよび大気海洋結合モデルによる20世紀ハインドキャスト実験を用いて評価した。
大蛇行時と非大蛇行時を比較すると、黒潮が大蛇行している時には(所謂、南岸)低気圧の主経路は南偏しており、大気海洋結合モデルで再現された黒潮の大蛇行においても同様な大気応答が
生じていることが見出された。黒潮の大蛇行は日本南岸の潜熱フラックスを減少させると共に、地表付近の傾圧帯の南方への遷移の原因となっている。海面熱フラックスの著しい減少は
黒潮大蛇行海域の低気圧の急速な発達を抑制し、結果的に下流側の海面更正気圧の上昇をもたらしている。
*Please refer to the following manuscript.
*詳細は下記論文を参照してください。
Hayasaki, M., R. Kawamura, M. Mori, and M. Watanabe (2013):
Response of extratropical cyclone activity to the Kuroshio large meander in northern winter. Geophysical Research Letters, 40, doi:10.1002/grl.50546